Python int() function is used to convert a given input to an integer.
This function is commonly used for type casting.
Syntax
int(value, base)
Parameters
- value(optional): The value you want to convert to an integer. This can be a string, a floating-point number, another integer, or any object that implements the __int__() method. The default is 0.
- base(optional): This specifies the base in which the string is formatted if value is a string. The default is 10.
Return value
It returns an integer object or raises an error if the conversion is not possible.
Example 1: Using with String
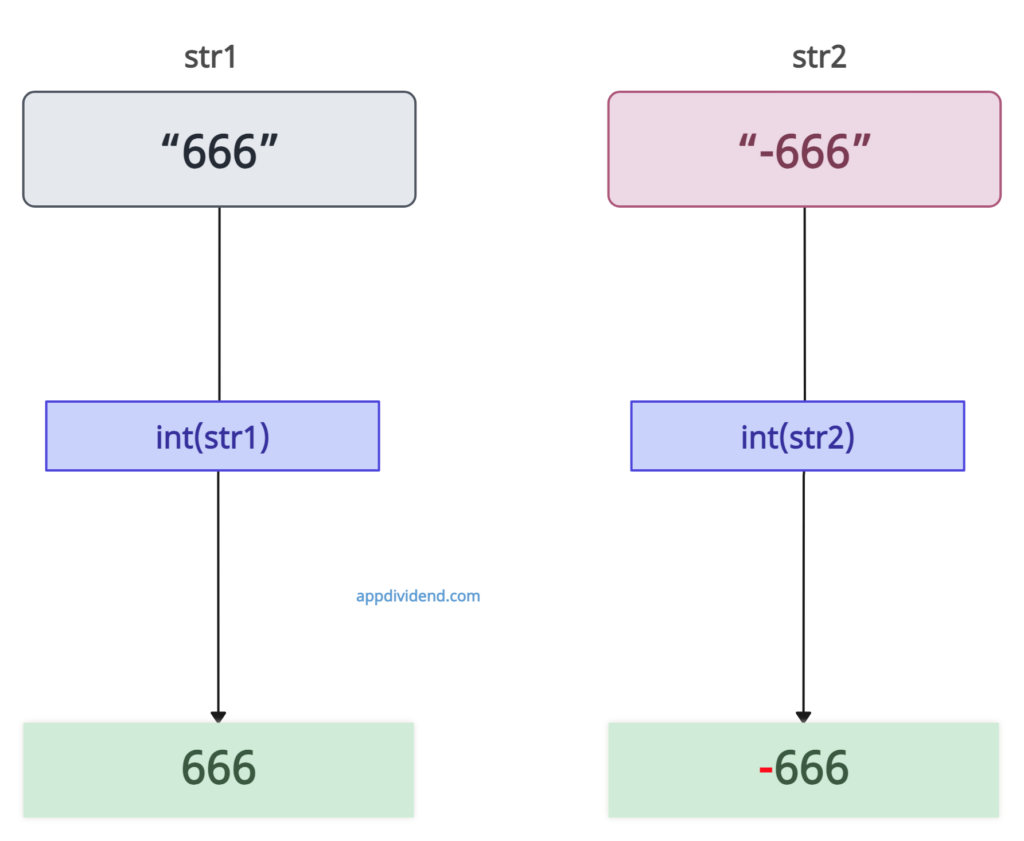
str1 = "666"
print(int(str1))
str2 = "-666"
print(int(str2))
Output
666
-666Example 2: Passing base parameter
print(int("1101", 2)) # Binary to decimal
print(int("2F", 16)) # Hexadecimal to decimalOutput
13
47
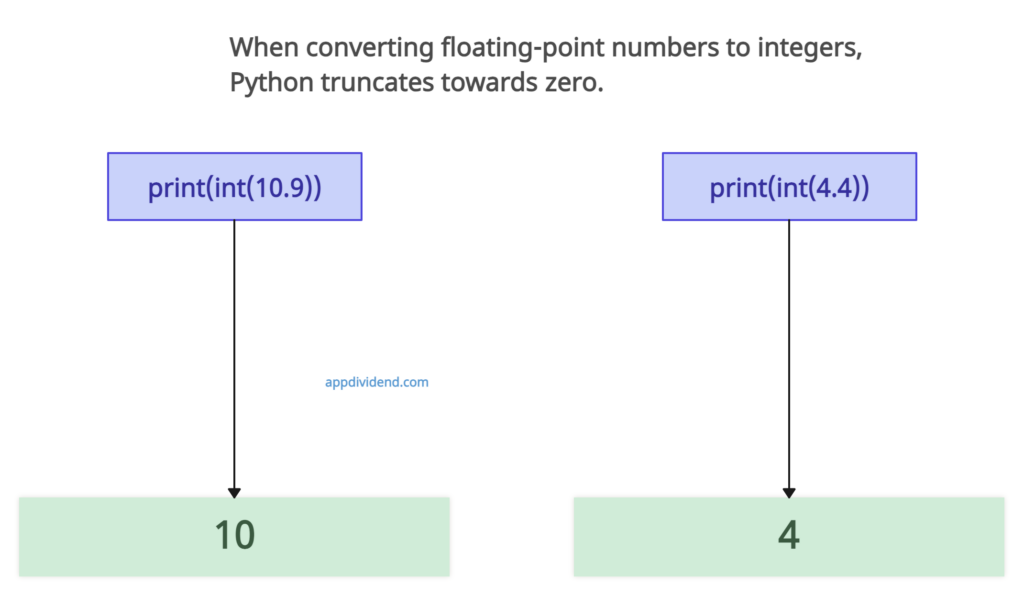
Example 3: Using with Float
print(int(10.9))
print(int(4.4))Output
10
4
Example 4: Using with Custom Objects
class Temperature:
def __init__(self, celsius):
self.celsius = celsius
def __int__(self):
# Return the temperature in Celsius as an integer
return int(self.celsius)
# Creating an instance of Temperature
temp = Temperature(26.7)
# Converting the temperature instance to an integer
print(int(temp))Output
26
Example 5: ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10
The ValueError is raised because the string “str1” cannot be interpreted as a decimal number, which is what the int() function expects by default.
print(int("str1"))
Output
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'str1'