The to_json() method in Pandas is used to convert a DataFrame into a JSON string.
Syntax
DataFrame.to_json(path_or_buf=None, orient=None,
date_format=None, double_precision=10,
force_ascii=True,
date_unit='ms',
default_handler=None, lines=False,
compression='infer', index=True)Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path_or_buf | The file path or object. If not specified, the result is returned as a string. |
| orient |
The format of the JSON string. Options include ‘split’, ‘records’, ‘index’, ‘columns’, and ‘values’.
|
| date_format | Determines the format of dates in the JSON output. Can be ‘epoch’ or ‘iso’. |
| double_precision | The number of decimal places for floating-point numbers. Defaults to 10. |
| force_ascii | Forces encoded strings to be ASCII. Defaults to True. |
| date_unit | The time unit to encode dates. Defaults to ‘ms’ (milliseconds). |
| default_handler | The handler to call if an object cannot be serialized. |
| lines | Writes the output as a JSON object per line if set to True. |
| compression | For on-the-fly compression of the output. Options include ‘infer’, ‘gzip’, ‘bz2’, ‘zip’, ‘xz’, ‘zstd’, None. ‘infer’ will use the extension path_or_buf for compression. |
| index | Includes the index in the JSON output. Defaults to True. |
| indent | Sets the indentation level for pretty-printed JSON. Defaults to None (no indentation). |
Return Value
This method returns a JSON string or writes the JSON to the file specified by path_or_buf.
When saving to a file, the method does not return the JSON string. Instead, it writes directly to the file.
Important points
- The “orient” parameter significantly changes the structure of the JSON output. It’s crucial to choose the right one based on your needs.
- The “lines” parameter is particularly useful when dealing with large data, allowing for more efficient streaming.
- When dealing with non-ASCII text, be cautious with the “force_ascii” parameter.
- The “compression” parameter is handy for reducing the size of the output file, especially with large DataFrames.
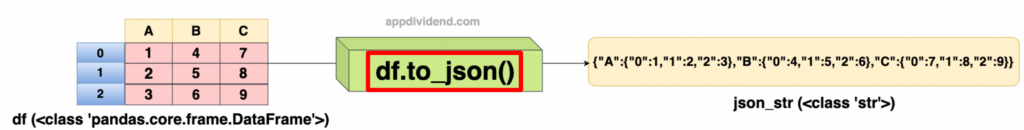
Example 1: Basic usage – Convert to JSON string
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json()
print(json_str)Output
{"A":{"0":1,"1":2,"2":3},"B":{"0":4,"1":5,"2":6},"C":{"0":7,"1":8,"2":9}}
Example 2: Specifying orientation
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json(orient='split')
print(json_str)
Output
{"columns":["A","B","C"],"index":[0,1,2],"data":[[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]}
Example 3: Specifying orient=”table”
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json(orient='table')
print(json_str)Output
{"schema":{"fields":[{"name":"index","type":"integer"},
{"name":"A","type":"integer"},
{"name":"B","type":"integer"},
{"name":"C","type":"integer"}],
"primaryKey":["index"],
"pandas_version":"1.4.0"},
"data":[{"index":0,"A":1,"B":4,"C":7},
{"index":1,"A":2,"B":5,"C":8},
{"index":2,"A":3,"B":6,"C":9}]}
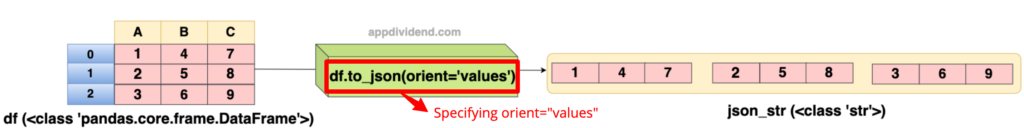
Example 4: Specifying orient=”values”
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json(orient='values')
print(json_str)
Output
[[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
Example 5: Specifying orient=”index”
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json(orient='index')
print(json_str)
Output
{"0":{"A":1,"B":4,"C":7},"1":{"A":2,"B":5,"C":8},"2":{"A":3,"B":6,"C":9}}
Example 6: Specifying orient=”records”
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
json_str = df.to_json(orient='records')
print(json_str)
Output
[{"A":1,"B":4,"C":7},{"A":2,"B":5,"C":8},{"A":3,"B":6,"C":9}]
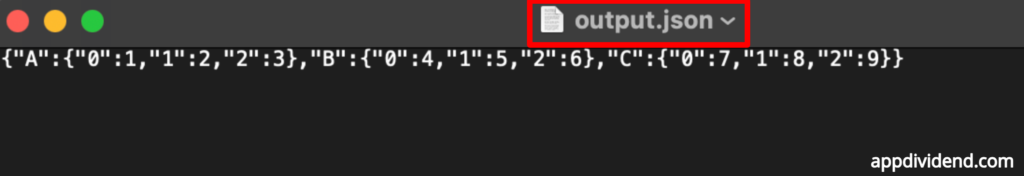
Example 7: Writing to a file
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]})
df.to_json('output.json')Output
That’s it.