JavaScript Math pow() method returns the base number raised to the power of the exponent number.
This method is particularly useful in scientific calculations, exponential growth calculations, and other mathematical operations involving powers.
Syntax
Math.pow(x, y)Parameters
- x(required): The base of the power.
- y(required): The exponent to which the base is raised.
Return Value
The value xy, i.e., x multiplied by itself y times.
- If the base is negative and the exponent is integral, the value returned is positive for even exponent values and negative for odd exponent values.
- If the base is negative and the exponent is fractional, the method will always return NaN.
- If the exponent is positive or negative zero, it will always return 1.
Visual Representation of Passing String Arguments
 Example 1: How to Use Math pow() Method
Example 1: How to Use Math pow() Method
console.log(Math.pow(4, 2)); //calculates 4 to the power of 2
console.log(Math.pow(4, -2)); //passing negative exponent
console.log(Math.pow(-4, 2)); //passing negative base
console.log(Math.pow(-4, -2)); //passing negative base and exponentOutput
16
0.0625
16
0.0625Example 2: Passing fractional values
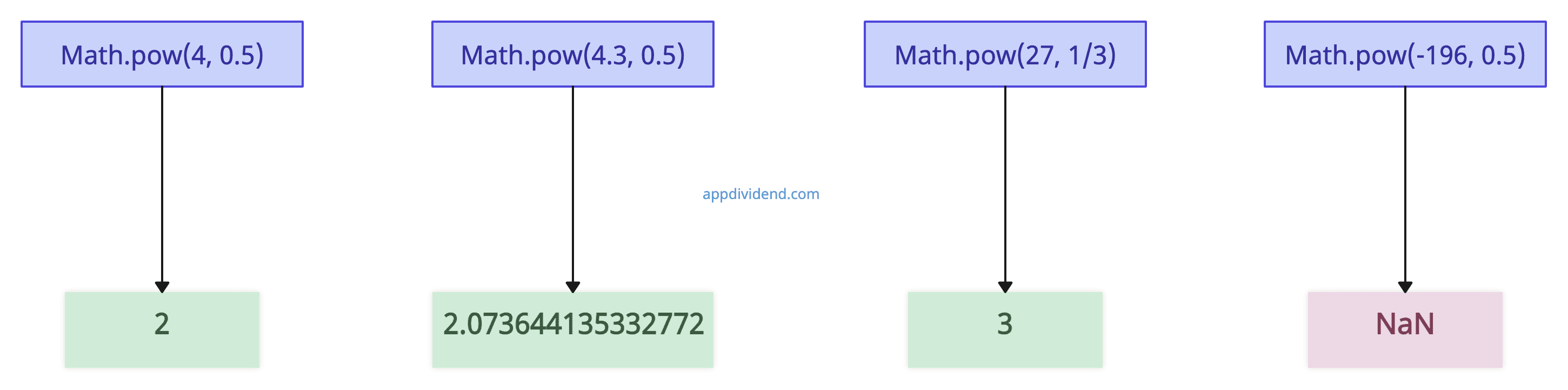
console.log(Math.pow(4, 0.5)); //square root of 4
console.log(Math.pow(4.3, 0.5)); //passing floating value
console.log(Math.pow(27, 1 / 3)); //cube root of 27
console.log(Math.pow(-196, 0.5)); //passing floating negative baseOutput
2
2.073644135332772
3
NaNExample 3: Passing 0 as an argument
console.log(Math.pow(4, 0));
console.log(Math.pow(0, 4));
console.log(Math.pow(0, 0)); Output
1
0
1Example 4: Passing String Arguments
let a = Math.pow("4", "2");
console.log(a);
let b = Math.pow("Will", "Smith");
console.log(b);
Output
16
NaN
Browser compatibility
- Google Chrome 1 and above
- Edge 12 and above
- Firefox 1 and above
- Opera 3 and above
- Safari 1 and above